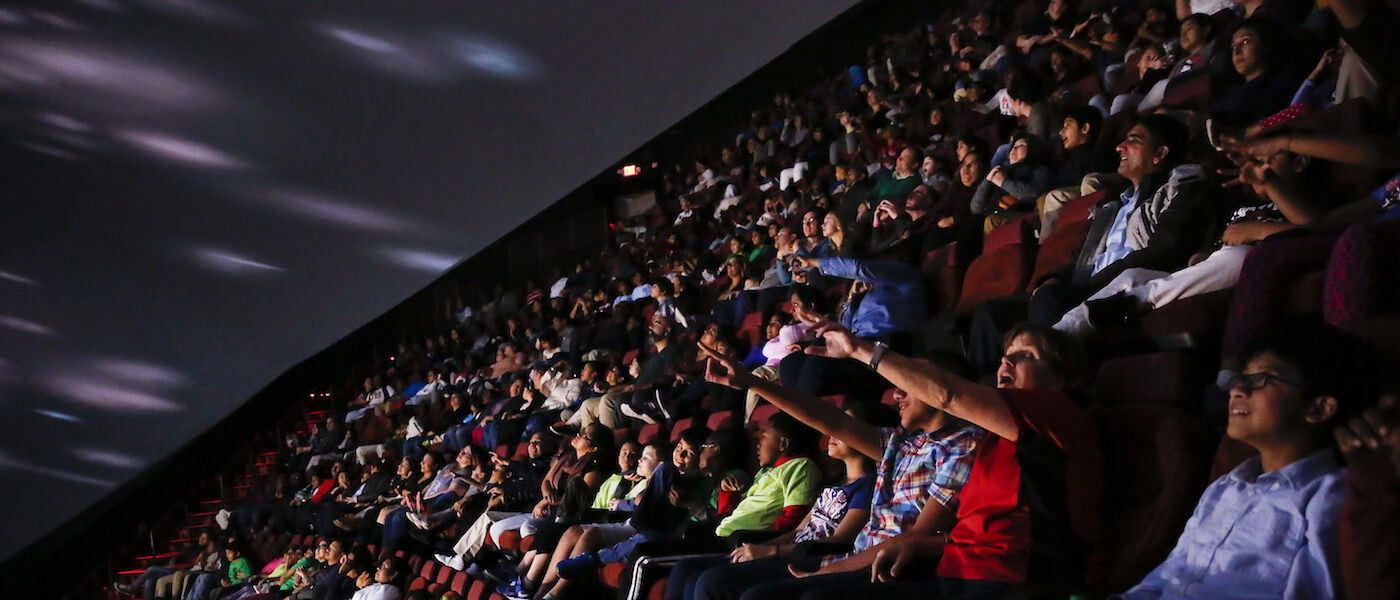Jennifer Chalsty Planetarium Educational Programs
LSC’s Jennifer Chalsty Planetarium is the largest in the Western Hemisphere.
Explore astronomy and space science in the immersive environment of our 89-foot dome or on your own screen. View stunning astronomical objects and celestial phenomena from Earth’s surface and then travel into space to explore them close up. Gain a better conceptual understanding by flying up to, around, and through the objects. Observe changes in Moon phases, reasons for the seasons, the nature of the planets, and tour the distant universe without ever leaving your seat!
Experience a planetarium show online or at LSC.
Please be advised that Liberty Science Center requires proof of COVID-19 vaccination for all visitors age 12 years and older. Click here to learn more.
Email us at groups@lsc.org for more details or to make a reservation. Please include your name, school or organization, group size, preferred dates and any other details or questions. An LSC team member will respond to you soon!
Grades Pre-K-2
One World, One Sky (30-45 Minutes)
Available at LSC. Join Big Bird and Elmo as they explore shapes in the sky and even go on a trip to the moon! Alignment to NJSLS - Science: 1-ESS1-1 Use observations of the sun, moon, and stars to describe patterns that can be predicted. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: W.1.8 With guidance and support from adults, recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question
Sun, Moon, and Stars (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Join a tour of the sky for our youngest astronomers! Explore the sun, moon, and stars and discover their patterns, including sunrise and sunset locations, moon phases, and how constellation visibility varies with Earth’s position from season to season. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: 1-ESS1-1 Use observations of the sun, moon, and stars to describe patterns that can be predicted. 1-ESS1-2 Make observations at different times of year to relate the amount of daylight to the time of year. 1-PS4-2. Make observations to construct an evidence-based account that objects can be seen only when illuminated. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: W.1.8 With guidance and support from adults, recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question.
Grades 3-5
All About Mars (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Mars has intrigued us for thousands of years. In this program, students will travel to Mars and explore the Red Planet as NASA sees it. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: 3-PS2-2 Make observations and/or measurements of an object’s motion to provide evidence that a pattern can be used to predict future motion. 4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns in rock formations and fossils in rock layers to support an explanation for changes in a landscape over time. 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: W.3.7 Conduct short research projects that build knowledge about a topic. W.4.7 Conduct short research projects that build knowledge through investigation of different aspects of a topic. (4-ESS1-1) Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
Black Holes (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Explore the nature of black holes, which are among the most mysterious objects in the universe. How do we know they exist? Where do they come from? What would it be like to get close to a black hole? Alignment to NJSLS - Science: 3-PS2-1 Plan and conduct an investigation to provide evidence of the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces on the motion of an object. 4-PS3-1 Use evidence to construct an explanation relating the speed of an object to the energy of that object. 5-PS1-1 Develop a model to describe that matter is made of particles too small to be seen. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: W.3.7 Conduct short research projects that build knowledge about a topic. W.4.2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas and information clearly. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
Pluto and the Deep Solar System (30-45 Minutes)
Available online only. Explore the objects at the farthest reaches of our solar system: Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto and the other dwarf planets. How were they discovered? What do we know about them? And why was Pluto reclassified from a planet to a dwarf planet? Alignment to NJSLS - Science: 3-PS2-2 Make observations and/or measurements of an object’s motion to provide evidence that a pattern can be used to predict future motion. 4-PS4-2 Develop a model to describe that light reflecting from objects and entering the eye allows objects to be seen. 5-PS1-3 Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. 5-ESS1-1 Support an argument that differences in the apparent brightness of the sun compared to other stars is due to their relative distances from Earth. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: W.3.7 Conduct short research projects that build knowledge about a topic. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.4 Model with mathematics. MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
Wonders of the Night Sky (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Use the current night sky to explore Earth and Space Science concepts. Topics relate to objects visible in the sky on the date of your program, including seasonal constellations and planets, exciting deep-sky objects, and breaking astronomical news. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: 3-PS2-2 Make observations and/or measurements of an object’s motion to provide evidence that a pattern can be used to predict future motion. 4-PS4-2 Develop a model to describe that light reflecting from objects and entering the eye allows objects to be seen. 5-ESS1-1 Support an argument that differences in the apparent brightness of the sun compared to other stars is due to their relative distances from Earth. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: W.3.7 Conduct short research projects that build knowledge about a topic. W.5.1 Write opinion pieces on topics or texts, supporting a point of view with reasons and information. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. MP.4 Model with mathematics.
Are We There Yet? (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Explore observations of the sun, planets, and stars to discover that objects in the universe are located at large distances from Earth and exhibit predictable cyclic patterns. See how large objects can appear very small when they are located far from Earth. Discover that the sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is close. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: 5-ESS1-1 Support an argument that differences in the apparent brightness of the sun compared to other stars is due to their relative distances from Earth. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: RI.5.7 Draw on information from multiple print or digital sources, demonstrating the ability to locate an answer to a question quickly or to solve a problem efficiently. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
Cycles of the Seasons (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Observe the repeating pattern of the seasons and learn how Earth’s tilt and orbit around the sun combine to change the length of day and night over the course of a year. See how Earth’s motion around the sun changes the stars visible from season to season. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: 5-ESS1-2 Represent data in graphical displays to reveal patterns of daily changes in length and direction of shadows, day and night, and the seasonal appearance of some stars in the night sky. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
Grades 6-8
All About Mars (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Three new missions arrived at Mars in early 2021. Explore the Red Planet, from an orange dot in the sky to the striking world we’ve seen through the eyes of our orbiters, landers, and rovers. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: MS-ESS1-3 Analyze and interpret data to determine scale properties of objects in the solar system. MS-PS2-4 Construct and present arguments using evidence to support the claim that gravitational interactions are attractive and depend on the masses of interacting objects. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: WHST.6-8.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
Asteroids: Discovery, Danger & Dinosaurs (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Investigate past asteroid impacts on Earth, from the extinction of the dinosaurs to a 2013 explosion over Russia, and look at what NASA is doing to track, study, and potentially divert other near-Earth asteroids. Then, explore how an asteroid led to the extinction of the dinosaurs 66 million years ago! Alignment to NJSLS - Science: MS-ESS1-3 Analyze and interpret data to determine scale properties of objects in the solar system. MS-ESS3-2 Analyze and interpret data on natural hazards to forecast future catastrophic events and inform the development of technologies to mitigate their effects. MS-ESS1-4 Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence from rock strata for how the geologic time scale is used to organize Earth’s 4.6-billion-year-old history. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: WHST.6-8.2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 6.RP.A.1 Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities.
Black Holes (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Explore the nature of black holes, which are among the most mysterious objects in the universe. How do we know they exist? Where do they come from? What would it be like to get close to a black hole? Alignment to NJSLS - Science: MS-ESS1-2 Develop and use a model to describe the role of gravity in the motions within galaxies and the solar system.
Cycles of the Seasons (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Observe the repeating pattern of the seasons and learn how Earth’s tilt and orbit around the sun combine to change the length of day and night over the course of a year. See how Earth’s motion around the sun changes the stars visible from season to season. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: MS-ESS1-1 Develop and use a model of the Earth-sun-moon system to describe the cyclic patterns of lunar phases, eclipses of the sun and moon, and seasons.
Phases and Eclipses (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Observe the changes in the moon’s phases as a month goes by and develop a conceptual model of their cyclic patterns, as well as of eclipses of the sun and moon. Explore these astronomical phenomena as seen from both Earth and outer space. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: MS-ESS1-1 Develop and use a model of the Earth-sun-moon system to describe the cyclic patterns of lunar phases, eclipses of the sun and moon, and seasons.
Pluto and the Deep Solar System (30-45 Minutes)
Available online only. Explore the objects at the farthest reaches of our solar system: Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto and the other dwarf planets. How were they discovered? What do we know about them? And why was Pluto reclassified from a planet to a dwarf planet? Alignment to NJSLS - Science: MS-ESS1-3 Analyze and interpret data to determine scale properties of objects in the solar system. MS-PS2-4 Construct and present arguments using evidence to support the claim that gravitational interactions are attractive and depend on the masses of interacting objects. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: WHST.6-8.1 Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
Wonders of the Night Sky (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Use the current night sky to explore Earth and Space Science concepts. Topics relate to objects visible in the sky on the date of your program and include seasonal constellations and planets, exciting deep-sky objects, and breaking astronomical news. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: MS-ESS1-3 Analyze and interpret data to determine scale properties of objects in the solar system. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 6.RP.A.1 Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities.
Grades 9-12
All About Stars (30-45 Minutes)
Available online only. Develop a conceptual model of the formation of the universe and the life cycle of a star. Use evidence from stellar light spectra, the motion of distant galaxies, the composition of matter in the universe, nuclear fusion, and the production of elements in stars to develop this model. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: HS-ESS1-1 Develop a model based on evidence to illustrate the life span of the sun and the role of nuclear fusion in the sun’s core to release energy that eventually reaches Earth in the form of radiation. HS-ESS1-2 Construct an explanation of the Big Bang theory based on astronomical evidence of light spectra, motion of distant galaxies, and composition of matter in the universe. HS-ESS1-3 Communicate scientific ideas about the way stars, over their life cycle, produce elements. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: SL.11-12.4 Present information, findings and supporting evidence clearly, concisely, and logically. The content, organization, development, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. HSN-Q.A.2 Define appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptive modeling.
Black Holes (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Explore the nature of black holes, which are among the most mysterious objects in the universe. How do we know they exist? Where do they come from? What would it be like to get close to a black hole? Alignment to NJSLS - Science: HS-ESS1-3 Communicate scientific ideas about the way stars, over their life cycle, produce elements. Connections to NJSLS – Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
The Solar System (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Tour all of the planets and many of the moons in the solar system, using the latest data from NASA. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: HS-ESS1-1 Develop a model based on evidence to illustrate the life span of the sun and the role of nuclear fusion in the sun’s core to release energy that eventually reaches Earth in the form of radiation. HS-ESS1-3 Communicate scientific ideas about the way stars, over their life cycle, produce elements. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: SL.11-12.4 Present information, findings and supporting evidence clearly, concisely, and logically. The content, organization, development, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. HSN-Q.A.2 Define appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptive modeling.
Wonders of the Night Sky (30-45 Minutes)
Available online or at LSC. Use the current night sky to explore Earth and Space Science concepts. Topics relate to objects visible in the sky on the date of your program and include seasonal constellations and planets, exciting deep-sky objects, and breaking astronomical news. Alignment to NJSLS - Science: HS-ESS1-1 Develop a model based on evidence to illustrate the life span of the sun and the role of nuclear fusion in the sun’s core to release energy that eventually reaches Earth in the form of radiation. HS-ESS1-3 Communicate scientific ideas about the way stars, over their life cycle, produce elements. Connections to NJSLS - English Language Arts: SL.11-12.4 Present information, findings and supporting evidence clearly, concisely, and logically. The content, organization, development, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. Connections to NJSLS - Mathematics: MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. HSN-Q.A.2 Define appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptive modeling.